To ping a Macbook, open Terminal and type “ping” followed by the target IP address or domain. Press Enter to start the ping test.
Pinging a Macbook allows you to test the connectivity between your computer and another device on a network. By sending packets of data and analyzing the response time, you can troubleshoot network issues and ensure a stable connection. In this guide, we will explore the steps to ping a Macbook efficiently and effectively.
Whether you are a novice user or a tech-savvy individual, understanding how to ping a Macbook can be a useful skill in managing and optimizing your network performance. Let’s dive into the process of pinging a Macbook and uncover its benefits in network diagnostics and troubleshooting.
What Is Pinging
Pinging is a network administration utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for a packet to reach the host and return.
Definition
Pinging is a command-line utility that is used to check if a specific IP address or a host is accessible and how long the trip takes. It sends a small packet of data to the target device and waits for a response.
Purpose
The primary purpose of pinging is to test and troubleshoot network connectivity. It can be used to determine the status of a network device, measure the response time of a network, and verify network connection.
Credit: www.macworld.com
Why Ping A Macbook
Wondering why ping a Macbook is necessary? Understanding the importance of testing network connectivity and checking for latency can help troubleshoot and optimize your internet connection. Below, explore how to properly ping a Macbook for network diagnostics.
Determine Network Connectivity
Ping command on a Macbook can verify if the device is connected to a network and identify any connection issues. This simple tool can quickly assess the status of your internet connection.
Check For Latency
Pinging your Macbook allows you to measure latency, the time it takes for data packets to travel between your device and a specified server. Low latency indicates a more responsive network connection.
Steps To Ping A Macbook
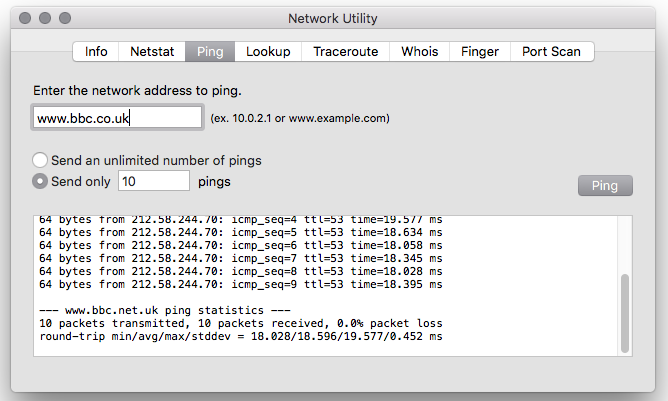
To ping a Macbook, open the Terminal app and type “ping” followed by the IP address or hostname. Press Enter to initiate the ping command and check the responses for connectivity status. This simple process helps troubleshoot network connectivity on a Macbook.
Steps to Ping a Macbook To ping a Macbook, you can use the Terminal application to send a signal to another device and check the connection between them. The process involves a few simple steps. Here is a basic guide on how to ping a Macbook. Open Terminal To begin, open the Terminal application on your Macbook. You can do this by searching for “Terminal” in the spotlight search or navigating to Applications > Utilities > Terminal. Enter Ping Command Next, in the Terminal window, type the following command: “ping [IP address or domain name]”. Replace [IP address or domain name] with the address of the device you want to ping. For example, if you want to ping Google, you would type: “ping google.com”. Interpreting the Results After entering the ping command, you will see a series of responses showing the status of the connection. You can check the results to see if the device is reachable and how long it takes for the signal to travel back and forth. By following these simple steps, you can easily ping a Macbook to test network connectivity and troubleshoot any connection issues.Common Ping Errors
When pinging a MacBook, you may encounter common errors that can hinder the process and cause frustration. Being aware of these errors and their potential solutions can help you troubleshoot more effectively. Here are some of the most common ping errors you may encounter:
Host Unreachable
When you encounter a “Host Unreachable” error while trying to ping a MacBook, it means that the host or destination you are trying to reach is not accessible. This could be due to a variety of reasons, such as incorrect network configurations or network connectivity issues. To resolve this error, ensure that the destination device is powered on and connected to the network. Verify the network settings on your MacBook to ensure they are correct. Additionally, check for any firewall or security settings that may be blocking the connection to the host.
Request Timed Out
Encountering a “Request Timed Out” error during a ping attempt means that the request to the destination device took too long to receive a response. This could be caused by network congestion, high latency, or a misconfigured firewall. To address this error, check for any network congestion or latency issues that may be affecting the connection. You can also try adjusting the firewall settings on the MacBook to allow the ping request to reach its destination.
Advanced Ping Options
In addition to the basic ping command, the macOS Terminal also provides a range of advanced options that can further enhance your troubleshooting abilities. These options allow you to customize the ping process according to your specific needs. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most useful advanced ping options available on your MacBook.
Changing Packet Size
By default, the ping command sends packets of data that are 56 bytes in size. However, you can modify the packet size to suit your requirements. This can be especially useful when you want to test how your network performs with different packet sizes.
To change the packet size, simply add the -s option followed by the desired packet size in bytes. For example:
ping -s 100 example.comThis will send packets of 100 bytes to the specified domain or IP address. Experimenting with different packet sizes can help you identify any potential issues or bottlenecks in your network.
Setting A Time Limit
Another useful option available with the ping command is the ability to set a time limit for each ping request. This allows you to determine how long the command will wait for a response before moving on to the next request.
To set a time limit, use the -t option followed by the desired timeout value in seconds. For example:
ping -t 5 example.comThis will limit each ping request to a maximum of 5 seconds. If a response is not received within this time frame, the ping command will move on to the next request. Setting a time limit can help you identify any network latency issues and pinpoint the source of the problem.

Credit: www.wikihow.com
Using Ping For Network Troubleshooting
When troubleshooting network issues on a Macbook, using the ping command can help identify connection problems. Simply open the Terminal and type “ping” followed by the IP address or domain name to test connectivity. This quick and efficient process can aid in pinpointing potential network issues.
Are you experiencing network issues with your MacBook? Don’t worry! Ping, a powerful command-line tool, can help you diagnose and troubleshoot network problems in no time. By sending small packets of data to a specific network address, you can test the connection and pinpoint the source of the issue. In this article, we will walk you through the process of using Ping for network troubleshooting on your MacBook.
Identifying Packet Loss
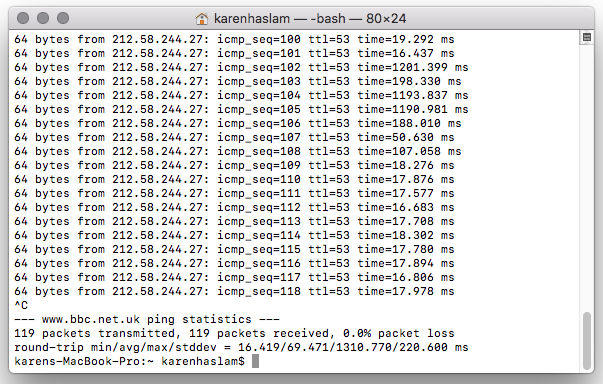
Packet loss is a common network problem that can cause disruption and slow down your internet connection. Fortunately, Ping is a fantastic tool for identifying packet loss. By sending multiple ping requests and analyzing the responses, you can determine if any packets are lost during transmission.
To identify packet loss, open the Terminal application on your Macbook (located in Applications/Utilities) and type the following command: ping -c 10 google.com. This command sends ten ping requests to the Google website. Keep an eye on the results. If you notice any lost packets, indicated by an asterisk or “Request timeout,” it means there is packet loss occurring.
Checking For Network Congestion
Network congestion can negatively affect your internet speed and overall network performance. Using Ping, you can check for any signs of network congestion on your MacBook. By measuring the time it takes for a ping request to reach its destination and return, you can assess the network’s latency or delay.
To check for network congestion, enter the following command in the Terminal: ping -c 10 apple.com. This command sends ten ping requests to the Apple website. Look for increased response times or high latency values, indicated by milliseconds (ms). If the average response time is consistently high, it could be a sign of network congestion.
Knowing how to use Ping for network troubleshooting is an essential skill for every MacBook user. It allows you to pinpoint the cause of network issues, whether it’s packet loss or network congestion. By understanding and interpreting the Ping results, you can take the necessary steps to resolve these problems and enjoy a smooth browsing experience.
Ping Vs. Traceroute
Understanding the difference between Ping and TraceRoute is crucial when it comes to troubleshooting network connectivity issues on your MacBook. Both tools can be effective in diagnosing network problems, but they are used in different scenarios. Let’s delve into the variations between these two utilities to grasp their unique roles in network diagnostics.
Difference Between Ping And Traceroute
Ping: This command is utilized to confirm whether a networked device is reachable. It assesses the round-trip time for data to travel to the target device and back. Ping simply determines if the target is reachable and how long it takes to receive a reply.
TraceRoute: Unlike Ping, TraceRoute displays the path that data packets take to reach a specific destination. It calculates the time taken for each hop and can pinpoint where a network connection might be failing. TraceRoute provides a more comprehensive understanding of the network route.
When To Use Each
Use Ping when you need to verify if a specific device is accessible and measure the time it takes for packets to travel. It is ideal for basic network connectivity tests and assessing latency.
On the other hand, TraceRoute should be employed when you need to identify the specific network hops that data packets are taking. It helps to troubleshoot connectivity issues by pinpointing the exact location of a network problem.
Credit: www.macworld.com
Ping On Macbook Vs. Windows
Ping On Macbook
Ping on Macbook allows users to test the stability and speed of their internet connection.
It measures the time it takes for data to travel from your device to a specific server and back.
Ping On Windows
Ping on Windows, similar to Macbook, helps to analyze network performance and troubleshoot connection problems.
It provides valuable insights into the quality of your connection in a simple and efficient way.
Frequently Asked Questions On How To Ping Macbook
How Do I Ping A Macbook?
Pinging a MacBook is simple. Open the Terminal app, type ‘ping’ followed by the IP address or hostname you want to test the connection with, and hit Enter. The ping utility will send some packets to the destination and display the response time.
Why Is It Important To Ping A Macbook?
Pinging a MacBook allows you to check the connectivity and response time with a specific IP address or hostname. It helps troubleshoot network issues, determine if a website or server is reachable, and assess the overall network performance.
How Can I Check The Ping Status Of My Macbook?
To check the Ping status of your MacBook, open the Terminal app and enter the command ‘ping’ followed by the IP address or hostname you want to test. The command will send ICMP echo request packets to the destination and display the response time and statistics.
What Is An Ip Address?
An IP address is a unique numerical identifier assigned to each device connected to a network. It allows devices to communicate and identify one another on the Internet or local network. IP addresses can be IPv4 (e. g. , 192.
168. 0. 1) or IPv6 (e. g. , 2001:db8::1).
Conclusion
To sum up, pinging your Macbook can help enhance your overall network performance. Whether it’s troubleshooting connectivity issues or optimizing your device’s connection speed, understanding how to ping your Macbook is a valuable skill. By following the simple steps outlined in this post, you can easily ping your Macbook and keep your network running smoothly.


0 comments