TBW SSD refers to the Total Bytes Written an SSD can handle before performance degradation. It’s an important factor in durability.
Solid State Drives (SSDs) have revolutionized storage technology with their incredible speed and reliability. Among the many specifications to consider when choosing an SSD, Total Bytes Written (TBW) is a crucial metric that determines the endurance and longevity of the drive.
Understanding what TBW SSD means can help users assess how much data can be written to the drive before it may start to experience performance issues. We will delve into the significance of TBW in SSDs, its impact on durability, and how it influences the selection process for storage solutions. Let’s explore the world of TBW SSD and unravel its importance in the realm of solid state drives.
Traditional Hard Drives Vs Ssds
TBW (Terabytes Written) is a measure used to determine the endurance of SSDs (Solid State Drives). It refers to the total amount of data that can be written to an SSD before it reaches its wear-out limit. Unlike traditional hard drives, SSDs have a limited TBW, which impacts their lifespan and longevity.
Traditional Hard Drives vs SSDs — Traditional spinning hard drives have been the primary storage medium for computers for many years. They rely on spinning disks to read and write data, while SSDs (Solid State Drives) are a newer technology that uses flash memory. Let’s compare the two in terms of storage technology, data access time, durability, and power consumption.Storage Technology
Traditional hard drives store data on spinning magnetic disks, while SSDs use flash memory to store data, resulting in faster data access times.Data Access Time
HDDs have longer data access times due to the mechanical movements involved in reading and writing data. SSDs, on the other hand, have faster data access times as they do not rely on moving parts.Durability
HDDs are more prone to physical damage due to their moving parts, whereas SSDs are more durable as they have no moving components.Power Consumption
HDDs consume more power due to the spinning disks and moving parts, while SSDs are more energy-efficient, resulting in longer battery life for laptops and less power usage for desktops. In summary, SSDs offer faster data access times, improved durability, and lower power consumption compared to traditional hard drives, making them a popular choice for many users.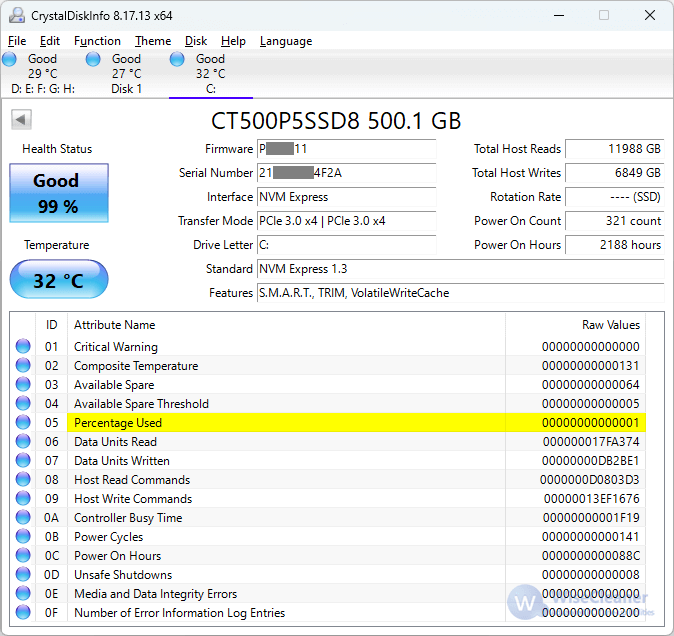
Credit: www.wisecleaner.com
Factors Affecting Tbw
TBW (Terabytes Written) is a measure of the endurance of Solid State Drives (SSDs), indicating the amount of data that can be written to the drive over its lifetime. Factors affecting TBW include drive capacity, workload intensity, and the type of NAND flash memory used.
Nand Flash Type
Drive Capacity
Write Amplification
Workload
Temperature
Factors Affecting Total Bytes Written (TBW) Ensuring SSD longevity is crucial due to NAND flash type, drive capacity, write amplification, workload, and temperature.Nand Flash Type
The type of NAND flash used impacts TBW due to variations in durability.Drive Capacity
Higher capacity drives tend to have higher TBW ratings due to more available NAND cells.Write Amplification
Reducing write amplification, or unnecessary write operations, can extend SSD lifespan.Workload
Heavy workloads lead to more write cycles and can decrease the SSD’s longevity.Temperature
High temperatures can accelerate NAND degradation, adversely affecting TBW. These factors play a crucial role in determining the reliability and durability of an SSD’s Total Bytes Written (TBW).Calculating Tbw For Ssds
When it comes to solid-state drives (SSDs), Total Bytes Written (TBW) is a crucial metric that indicates the endurance and lifespan of the drive. Knowing how to calculate TBW can help you assess the longevity and performance of your SSD.
Formula For Calculating Tbw
The formula to calculate Total Bytes Written (TBW) for an SSD is:
TBW = Capacity x DWPD x 365 x Write Amplification Factor- TBW: Total Bytes Written
- Capacity: The storage capacity of the SSD in gigabytes
- DWPD: Drive Writes Per Day, indicating the number of times you can write the total capacity of the drive each day
- Write Amplification Factor: A factor that represents the efficiency of the SSD’s write operations
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a 1TB (1000GB) SSD with a DWPD of 0.3 and a Write Amplification Factor of 2:
- Calculate TBW:
TBW = 1000 x 0.3 x 365 x 2 = 219,000 TBW
In this case, the SSD has a Total Bytes Written (TBW) of 219,000, indicating the total amount of data that can be written to the drive over its lifespan.
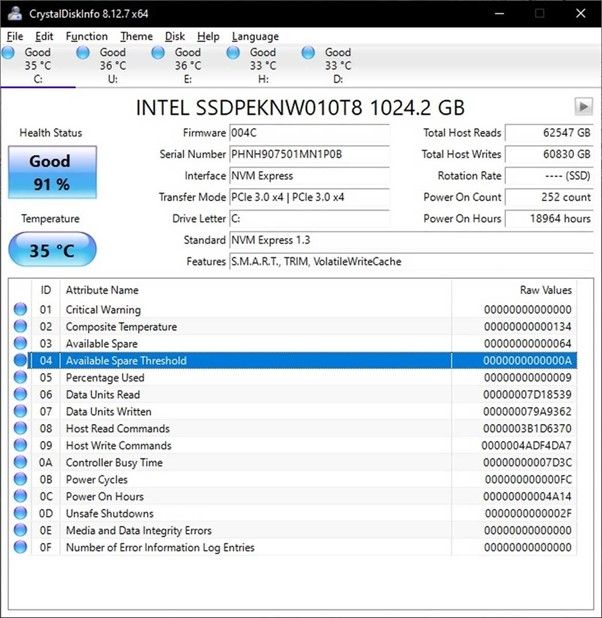
Credit: www.easeus.com
Tbw Ratings In Ssd Specifications
When it comes to understanding solid-state drives (SSDs), one important specification to consider is the TBW rating. This specification is essential in assessing the durability and longevity of an SSD. TBW stands for Terabytes Written, which refers to the total amount of data that can be written to the drive over its lifespan.
Importance Of Tbw Rating
The TBW rating plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of an SSD for specific tasks and workloads. It provides an estimate of how many terabytes of data can be written to the drive before it is likely to experience failure or a significant decrease in performance. This information is particularly vital for businesses and individuals who rely on SSDs for heavy writing workloads, such as video editing, database management, and large-scale content creation.
Comparing Tbw Ratings
When comparing SSDs, the TBW rating serves as a comparative measure of durability and endurance. Higher TBW ratings indicate that an SSD can withstand greater write loads over its lifetime, making it suitable for intensive usage scenarios. By understanding and comparing TBW ratings, consumers can make informed decisions about which SSD is best suited for their intended usage, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Effect On Drive Lifespan
The TBW rating directly influences the overall lifespan of an SSD. A higher TBW rating generally results in an extended lifespan for the drive, as it can withstand more write operations without experiencing degradation. Conversely, a lower TBW rating may limit the SSD’s ability to sustain heavy writing workloads, potentially leading to a shorter lifespan and the need for more frequent replacements.

Credit: techcommunity.microsoft.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is Tbw Ssd
What Is Tbw Ssd?
TBW SSD stands for Terabytes Written Solid State Drive. It refers to the total amount of data that can be written to an SSD before the drive reaches its endurance limit. This measurement is important to consider when choosing an SSD for heavy workloads or high data transfer rates.
Pick an SSD with a higher TBW rating for a longer lifespan.
Conclusion
In understanding what TBW SSD is, we’ve seen its role in ensuring data reliability and endurance. Its impact on storage and performance cannot be overstated. As technology continues to evolve, it’s clear that SSDs, with their exceptional TBW ratings, are here to stay.
Embracing this innovation is crucial for staying ahead in the digital landscape.

0 comments